Time needed: 25 days, 10 hours and 23 minutes
Explore interactive multimedia description and composition
- Introduction to interactive multimedia
Interactive multimedia refers to digital content that combines various forms of media, such as text, images, audio, video, and animations, in a way that allows users to interact with and engage with the content. It is characterized by its ability to respond to user input, making the user’s experience dynamic and engaging.

Categories included in interactive multimedia
- E-Learning and Education:
- Interactive Tutorials: Online courses and tutorials that use interactive multimedia to facilitate learning.
- Educational Games: Games designed to educate while engaging users in learning activities.
- Simulations: Realistic simulations for training and educational purposes.
- Entertainment and Gaming:
- Video Games: Interactive multimedia games for entertainment and storytelling.
- Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality: Immersive experiences that combine the real and virtual worlds.
- Interactive Storytelling: Narrative experiences where user choices affect the outcome.
- Digital Art and Creativity:
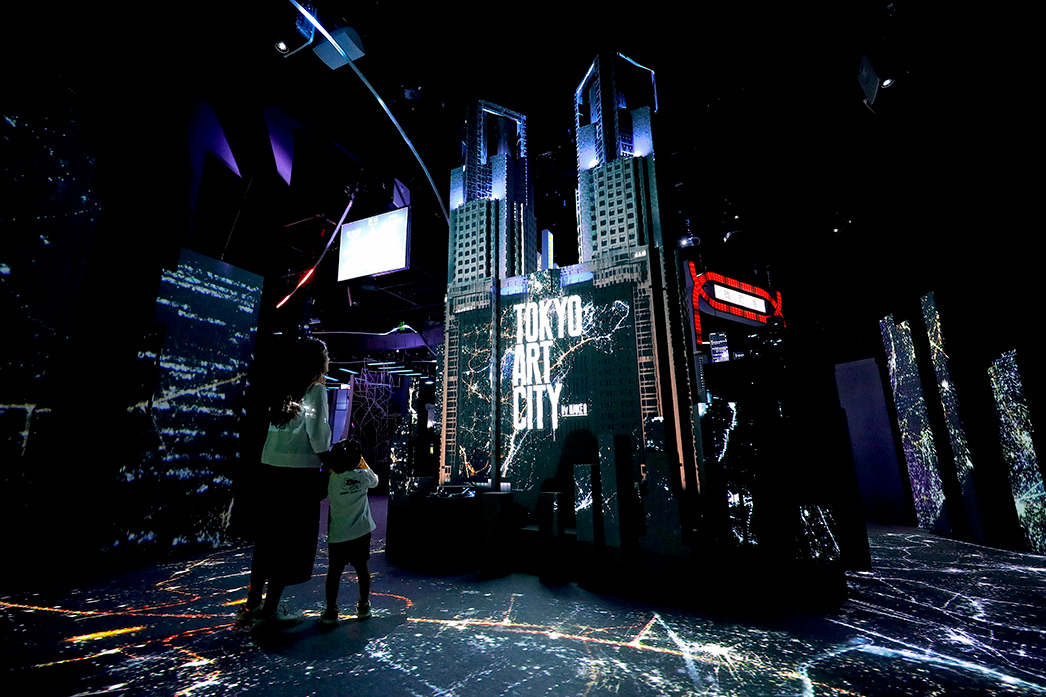
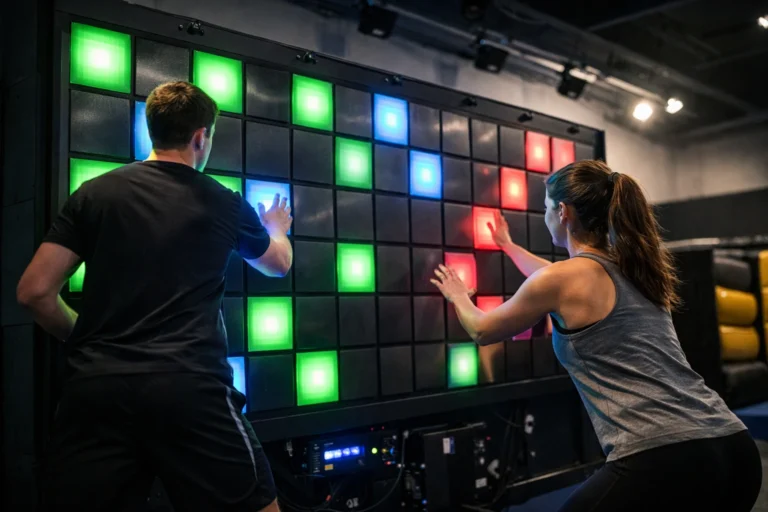
- Interactive Art Installations: Artistic installations that respond to user interactions.
- Creative Software: Tools for digital art, animation, and music production.
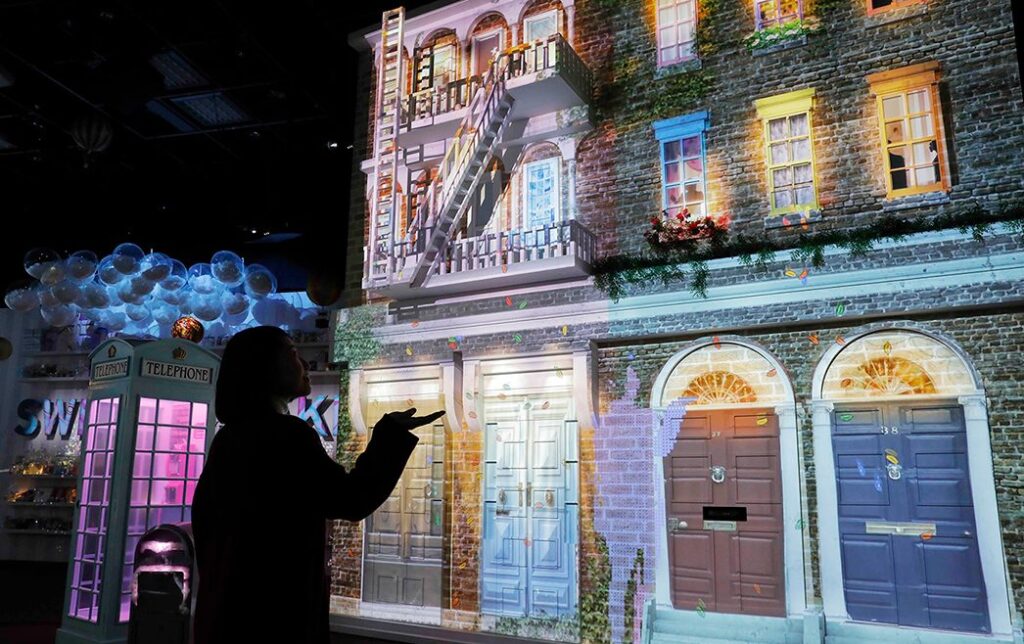
- Interactive Exhibitions: Museums and galleries that incorporate multimedia for interactive displays.
- Marketing and Advertising:
- Interactive Ads: Online advertisements that engage users with multimedia content.
- Product Demos: Interactive demonstrations of products or services.
- Virtual Tours: 360-degree tours of real estate, travel destinations, or businesses.
- Web and User Interfaces:
- Website Interactivity: Websites that use multimedia for user engagement.
- User Experience (UX) Design: Designing interactive interfaces for a smooth user experience.
- Interactive Prototyping: Creating interactive prototypes for product design.
- Healthcare and Medicine:
- Medical Simulations: Interactive tools for medical training and diagnosis.
- Rehabilitation: Interactive multimedia used in physical and cognitive rehabilitation.
- Telemedicine: Multimedia for remote doctor-patient interactions.
- Cultural and Heritage Preservation:
- Virtual Museums: Online museums with interactive exhibits and collections.
- Archaeological Reconstructions: Interactive multimedia to explore historical sites.
- Training and Simulation:
- Military and Defense: Simulation and training for military operations.
- Flight Simulation: Training pilots with realistic flight simulators.
- Corporate Training: Interactive multimedia for employee training.
- Data Visualization:
- Interactive Dashboards: Visualizing and interacting with data for business or research.
- Infographics: Interactive infographics for data presentation.
- Geospatial Visualization: Mapping and geographic information systems (GIS).
- Social and Communication:
- Video Conferencing: Interactive multimedia tools for online meetings and collaboration.
- Social Media: Platforms with multimedia features for sharing and engaging with content.
- Interactive Chatbots: AI-driven interactive chat systems for customer service.
- Gaming and Simulation Software Development:
- Game Development: Creating video games with interactive elements.
- Simulation Software: Developing simulations for training and analysis.
- Serious Games: Games designed for educational or professional purposes.
Linear Multimedia:Linear multimedia follows a predefined and fixed sequence of content delivery. Users have limited control over the progression of the content, and it typically plays in a linear, uninterrupted manner.
Hypermedia:Hypermedia, short for “hyperlinked multimedia,” offers users the ability to navigate content using hyperlinks or interactive elements. Users can choose their path through the multimedia content, making it non-linear.
Non-Linear Multimedia: Non-linear multimedia combines elements of both linear and hypermedia content. Users have some degree of control over the content’s progression, but the narrative or structure may still maintain a central storyline.